業內快訊
棕色脂肪(BAT)與2型糖尿病、血脂異常、冠狀動脈疾病、腦血管疾病、充血性心力衰竭和高血壓等方面的潛在作用
 時間:2021-01-05
時間:2021-01-05
 來源:
來源:
 瀏覽量:1844
瀏覽量:1844
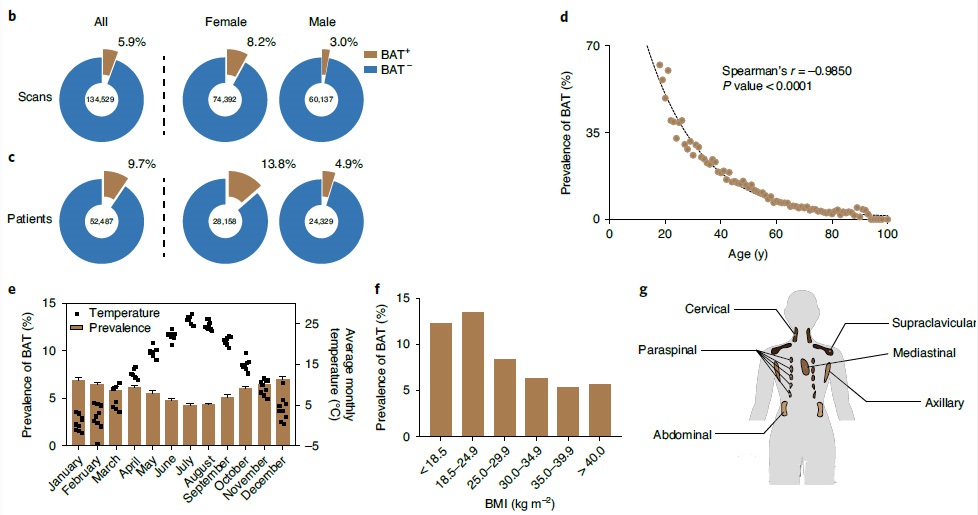
2021年1月4日,《Nature Medicine》刊登了[Brown adipose tissue is associated with cardiometabolic health],由美國洛克菲勒大學領導的研究團隊為我們提供了強有力的證據:在對超過52000名參與者的分析顯示,那些檢測到棕色脂肪的人,患2型糖尿病、血脂異常、冠狀動脈疾病、腦血管疾病、充血性心力衰竭和高血壓等疾病的可能性要低得多。

White fat stores excess energy, whereas brown and beige fat are thermogenic and dissipate energy as heat. Thermogenic adipose tissues markedly improve glucose and lipid homeostasis in mouse models, although the extent to which brown adipose tissue (BAT) influences metabolic and cardiovascular disease in humans is unclear. Here we retrospectively categorized 134,529 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography–computed tomography scans from 52,487 patients, by presence or absence of BAT, and used propensity score matching to assemble a study cohort. Scans in the study population were initially conducted for indications related to cancer diagnosis, treatment or surveillance, without previous stimulation. We report that individuals with BAT had lower prevalences of cardiometabolic diseases, and the presence of BAT was independently correlated with lower odds of type 2 diabetes, dyslipidemia, coronary artery disease, cerebrovascular disease, congestive heart failure and hypertension. These findings were supported by improved blood glucose, triglyceride and high-density lipoprotein values. The beneficial effects of BAT were more pronounced in individuals with overweight or obesity, indicating that BAT might play a role in mitigating the deleterious effects of obesity. Taken together, our findings highlight a potential role for BAT in promoting cardiometabolic health.
洛克菲勒大學的研究團隊與紀念斯隆凱特琳癌癥中心的醫生合作,對2009年6月至2018年3月期間的52487患者超過13萬份的PET掃描結果進行了分析,發現5070個患者(9.7%)體內被檢測到棕色脂肪,女性比男性更為常見,并隨著年齡增長而減少。研究人員在6個部位(頸部、鎖骨上、腋窩、縱隔、椎旁和腹部)測量了棕色脂肪的活性,發現頸部和鎖骨上的棕色脂肪最多。這與先前的研究結果一致。
但Cohen指出,這一數字可能被低估了,因為患者在檢查前被指示避免寒冷暴露、運動和攝入咖啡因,所有這些都被認為會增加棕色脂肪的活性。
研究人員發現,幾種常見和慢性疾病在可檢測到棕色脂肪的人群中較不常見。例如,檢測到棕色脂肪的人群中,只有4.6%的人患有2型糖尿病;而在沒有檢測到棕色脂肪的人群中,這一比例為9.5%;同樣,檢測到棕色脂肪的人群中,18.9%的人膽固醇異常,而沒有棕色脂肪的人這一比例為22.2%。
此外,這項研究還揭示了另外三種情況,即檢測到棕色脂肪的人群中,高血壓、充血性心力衰竭和冠狀動脈疾病的風險較低,這在以前的研究中是沒有觀察到的。
還有一個令人驚訝的發現,棕色脂肪可能減輕了肥胖對健康的負面影響。一般來說,肥胖的人患心臟病和代謝疾病的風險會增加。但研究人員發現,在檢測到棕色脂肪的肥胖人群中,這些情況的患病率與非肥胖者相似。Cohen說:“看起來它們幾乎不受白色脂肪的有害影響。”
棕色脂肪促進健康的實際機制目前還不清楚,但已有一些線索。例如,棕色脂肪細胞消耗葡萄糖來燃燒熱量,這可能會降低血糖水平,而血糖水平是患糖尿病的主要風險因素。
另外,棕色脂肪的作用在高血壓等與激素系統密切相關的其他疾病中更為神秘。
Cohen說:“我們正在考慮這樣一種可能性:棕色脂肪組織不僅消耗葡萄糖和燃燒熱量,而且可能還參與了向其他器官傳導激素信號。”
該研究團隊正計劃進一步研究棕色脂肪的生物學,包括尋找可能解釋為什么有些人比其他人擁有更多棕色脂肪的遺傳變異,這可能是開發刺激棕色脂肪活性的藥理學方法來治療肥胖癥和相關疾病的第一步。